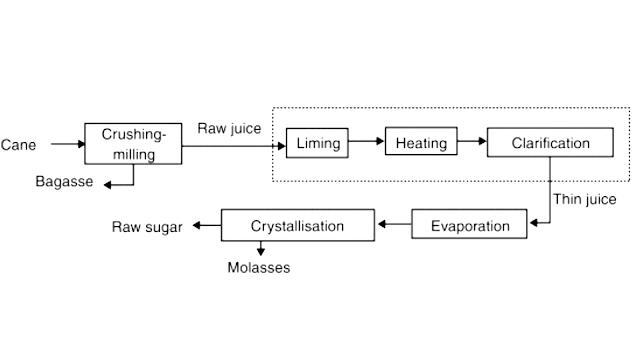
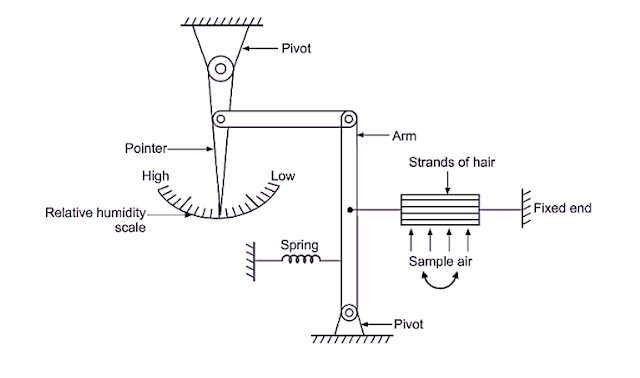
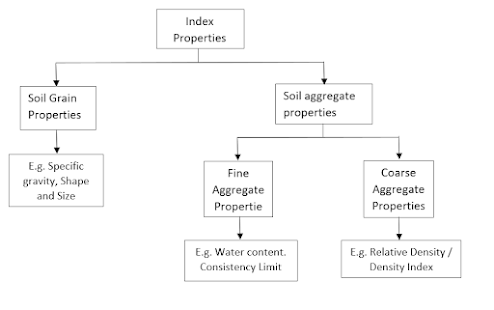
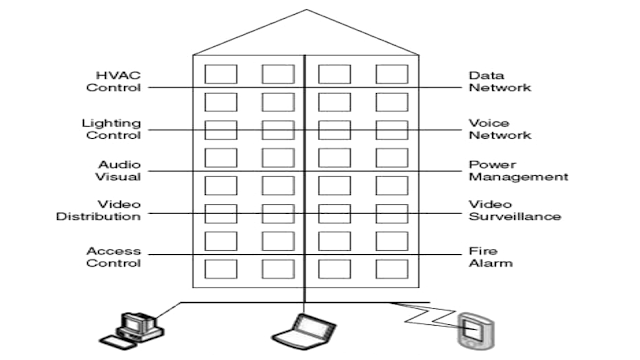
What is Indicator and its Example
What is Indicator and its Example Indicator Essentially an indicator is a common auxiliary device and is used to provide a human readable indication of an instrument signal. And an inductor is basically a distance amplifier. Inductors are used to accurately measure small distances or angles. The indicator gives the human operator a convenient way to see what the output of the transmitter is without connecting test equipment. Furthermore, the indicators can be located away from their respective transmitters, providing a readout at a location more convenient than the location of the transmitter. Indicators are a measuring tool so they are used to indicate. And to understand what the data on the indicators actually shows, some basic understanding of elementary statistics is required. Also the ability to understand the data will help you adjust, challenge or change the indicators being used. A good indicator is a measure of an excellent system. Indicative Example Temperature Indicator The