Pressure switch
Pressure switch
A pressure switch is a form of switch that operates an electrical contact when a certain set fluid pressure has been reached on its input. The switch may be designed to make contact either on pressure rise or on pressure fall.
Pressure Switches are devices that are configured to sense a change in pressure and respond in a specified manner.
A pressure switch turns an electric circuit ON or OFF at a preset pressure.
The pressure is the set point of the Switch.
Pressure Switch is used in some form of control.
The pressure switch is usually a micro Switch or mercury Switch.
The pressure is fed to the inside of a bellows which carries a contact plate.
The contact plate touches contact point.
The pressure switch can be modified so as to make a low pressure contact in addition to high pressure contact.
Most switches contain two sets of contacts, one normally open and the other normally closed.
Uses of Pressure Switch
- Pressure switch uses as limiting the pressure.
- The pressure switch is used to operate a safety valve which vents steam when the pressure exceeds the upper limit.
- Another important user of the pressure switch is in the computer panel.
- In the computer panel blowers are used for cooling purposes.
- Whenever the blower fails due to any reason a pressure switch is actuated which cuts off the power supply of the panel.
- The computer panel components are protected from the high temperature which can occur due to failure of the blower.
Types of pressure switch
Electromechanical pressure switch
The most common electromechanical pressure switches are composed of a
Sensing element
Electrical snap-action Switch
Specifications of Electromechanical pressure switch
Lesser life cycle.
Low accuracy.
Lesser frequency response.
Short-term stability.
Low resistance to shock and vibration.
Ability to handle a lesser range of system pressures.
Solid state pressure switch
Solid-state pressure so contains following characteristics
One to four or more Switch points.
Digital displays.
Analog and digital outputs.
Full programmability.
Provide a proportional 4-20 mA analog signal or digital output.
Specifications of solid-state pressure switch
Longer life cycle about 100 million cycles.
High accuracy.
A broad frequency response.
Long-term stability.
High resistance to shock and vibration.
Ability to handle a wide range of system pressures.
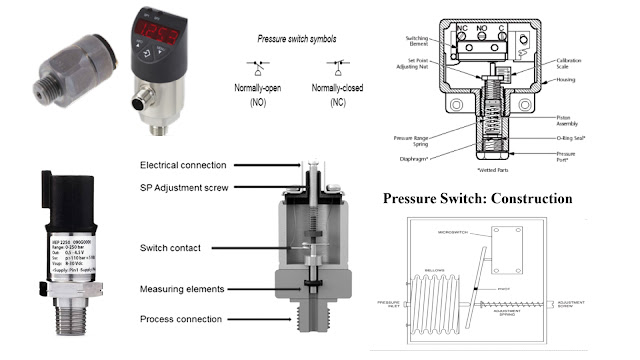
Construction
Pressure switch is a switch designed to monitor a process pressure & provide an
output when a set pressure (set point) is reached. A pressure switch does this by
applying the process pressure to a bellows (as a sensing element) to generate a force
which is compressed of a pre-compressed range spring.
Working
As shown in sectional view of the pressure switch above, the inlet pressure is applied
to the bottom of the operating piston. This piston is forced upwards by the inlet
pressure against the range spring. The tension of the range spring can be adjusted so
that it is compressed at a certain pressure or set point. When this pressure is reached,
the operating pin will hit the trip button on the microswitch and change it over.
The normally open contacts (NO to C) will become closed and normally closed
contacts (NC to C) will open. The pressure at which the micro switch changes over is
set by adjusting the trip setting nut. This nut adjusts the tension of the range spring
(eg. If the nut is turned clockwise the trip pressure will be higher)
Micro switch
The micro switch is used to make or break an electrical circuit when the pressure
switch operates. It is made up of NC and NO, when switch is operates the NO contact
become close and the NC becomes open.
Symbol
Applications
Pressure switches in their simple form detect a pressure change and at a predetermined level or set point open or closed a contact. They act as
- Safety devices.
- Alarms.
- Control elements within a system.
- Steam power plant.
- Electric motors.
- Gas compressor.
- Automobiles.
- Pumps.
- Boilers.
- Steam turbines.
- Hydraulic Surge.
- Power Generation Plant.


Comments
Post a Comment