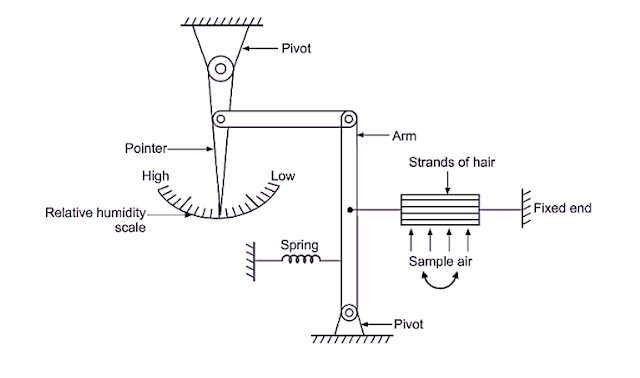
How to Install and Select a Proximity Sensor
How to Install and Select a Proximity Sensor Proximity sensors are used to detect the presence or absence of an object without any physical contact . The selection depends on the type of object , sensing distance , and installation environment . There are four type like Inductive Proxy sensor, Capacitive proxy sensor, Photoelectrical Proxy sensor, Ultrasonic Proxy sensor. 1. Inductive Proximity Sensor Working Principle: Detects metallic objects using an electromagnetic field . Detection Range: Up to 50 mm (depending on size and target material). Applications: Metal detection, machine automation, position sensing. Installation Tips: Mount flush or non-flush as per manufacturer guidelines. Avoid nearby metallic objects that cause false triggering. Ensure correct alignment with the target metal surface. 2. Capacitive Proximity Sensor Working Principle: Detects metallic and non-metallic obj...

.png)