Soil Moisture Sensor working principle and applications
Soil Moisture Sensor
What is a Soil Moisture Sensor?
The soil moisture sensor is one kind of sensor used to gauge the volumetric content of water within the soil. As the straight gravimetric dimension of soil moisture needs eliminating, drying, as well as sample weighting. These sensors measure the volumetric water content not directly with the help of some other rules of soil like dielectric constant, electrical resistance, otherwise interaction with neutrons, and replacement of the moisture content.
The relation among the calculated property as well as moisture of soil should be adjusted & may change based on ecological factors like temperature, type of soil, otherwise electric conductivity. The microwave emission which is reflected can be influenced by the moisture of soil as well as mainly used in agriculture and remote sensing within hydrology.
These sensors normally used to check volumetric water content, and another group of sensors calculates a new property of moisture within soils named water potential. Generally, these sensors are named as soil water potential sensors which include gypsum blocks and tensiometer.
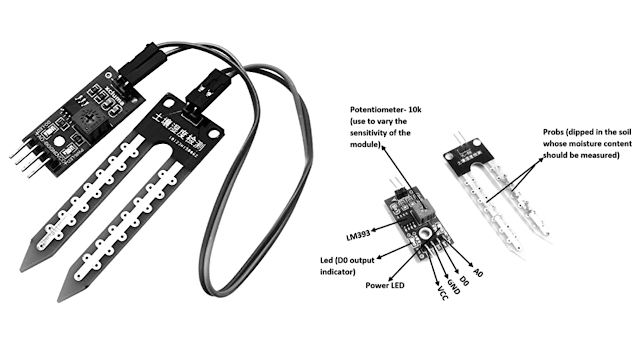
Soil Moisture Sensor Pin Configuration
The FC-28 soil moisture sensor includes 4-pins
- VCC pin is used for power
- A0 pin is an analog output
- D0 pin is a digital output
- GND pin is a Ground
This module also includes a potentiometer that will fix the threshold value, & the value can be evaluated by the comparator-LM393. The LED will turn on/off based on the threshold value.
How the Sensor Works
The Soil Moisture Sensor uses capacitance to measure dielectric permittivity of the surrounding medium. In soil, dielectric permittivity is a function of the water content. The sensor creates a voltage proportional to the dielectric permittivity, and therefore the water content of the soil.
The sensor averages the water content over the entire length of the sensor. There is a 2 cm zone of influence with respect to the flat surface of the sensor, but it has little or no sensitivity at the extreme edges. The figure above shows the electromagnetic field lines along a cross-section of the sensor, illustrating the 2 cm zone of influence.
Working Principle
This sensor mainly utilizes capacitance to gauge the water content of the soil (dielectric permittivity). The working of this sensor can be done by inserting this sensor into the earth and the status of the water content in the soil can be reported in the form of a percent.
This sensor makes it perfect to execute experiments within science courses like environmental science, agricultural science, biology, soil science, botany, and horticulture.
Specifications
- The required voltage for working is 5V
- The required current for working is <20mA
- Type of interface is analog
- The required working temperature of this sensor is 10°C~30°C
Soil Moisture Sensor Applications
- Agriculture
- Landscape irrigation
- Research
- Simple sensors for gardeners

ReplyDeleteThanks for this wonderful blog. As I read the whole information and easily comes to know that how this sensor works and which principle used in it. All the information and diagrams can really helpful for anybody because by reading following this information anyone can easily understand this information. Ubitrack also provides such kind of instruments which is used for tracking etc. So anyone who wants to buy these kinds of products can contact them at Ubitrack.com