Flow switch working principle and types
Flow Switch
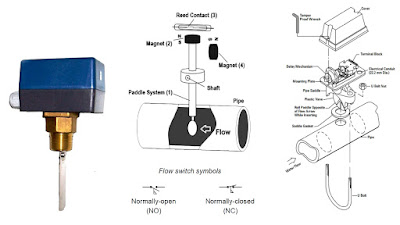
A flow switch is one detecting the flow of some fluid through a pipe. Flow switches often use “paddles” as the flow-sensing element, the motion of which actuates one or more switch contacts. A flow switch, like all switches, is a device designed to make and break an electric current in a circuit. In an industrial system, a flow switch is essential in monitoring and controlling the flow rate of process media – such as steam, liquids, and gases. Flow switches help maintain safe and manageable rates of flow by triggering actions in various machines within a system to provide on/off flow control of process media.
Principle of Flow Switch
The “normal” status of a switch is the resting condition of no stimulation. A flow switch will be in its “normal” status when it senses minimum flow (i.e. no fluid moving through the pipe). For a flow switch, “normal” status is any fluid flow rate below the trip threshold of the switch.


Working of the flow switch
Firstly the connected paddles activate the flow switches. As water and gas passes, the connected paddle gets displaced. The switch will automatically lock the circuit off when the substance’s volume will be too high and too low. It is done to prevent any damage to the system.
Different types of flow switch
- Paddle flow switch
- Shuttle / Piston flow switch
- Thermal flow switch
- Piezo flow switch
1. Paddle flow switch
Paddle flow switches or vane sensors with an electrical contact output are at a specific flow rate. Dwyer flow switches are economical and reliable. Applications include proof of boiler flow, air conditioning, controlling of dampers according to flow, and protecting pumps, motors and other equipment against low or no flow.
2. Shuttle / Piston flow switch
Shuttle or piston flow switches are sensors with an electrical contact output at a specific flow rate. Models are used with oil, air, water and gases. Applications include oil flow control, low flow detection in cooling lines, and high pressure lubrication systems. Rugged construction and excellent chemical compatibility simplify flow/no flow detection.
3. Thermal flow switch
Thermal flow switches are sensors with an electrical contact output at a specific flow rate. Dwyer models provide a complete system for leak detection and feature a selectable NO or NC operation. Applications include chillers, hot water heaters, and liquid transfer systems.
4. Piezo flow switch
Piezo flow switches are sensors with an electrical contact output. The bulk flow monitor provides effective monitoring for most flow/no flow conditions in pipes. Applications include oil spray systems, rotary drums, distributors, and food processing. Dwyer's piezo flow switch offers many features that exceed the industry standards.
Questions and Answers
1. How Does a Flow Switch Work?
Answer: There are a variety of different types of flow switches on the market today – functioning in a variety of different ways – but what all flow switches have in common is that when the flow rate reaches a switch’s set-point, it can either open or close the circuit which triggers an action: whether it’s turning a pump on or off or it’s actuating an alarm.
Flow switches are either configured to be Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC). This refers to the default state of the switch. With a NO switch, the circuit is open (OFF) until triggered otherwise. With a NC switch, the circuit is closed (ON) until triggered otherwise.
2. What is Flow?
Answer: In industrial processing, flow is the movement of liquids, steam, and gases through a processing system. Flow rate measurement is used to measure the volume of fluid process media passing through a specific cross-sectional area per unit of time. Monitoring flow rate measurements is essential in controlling the safe movement of fluid within an industrial system. The monitoring and control of flow is a requirement for all industries that process fluid media.
3. What is a Flow Switch Used For?
Answer: As previously stated, flow switches are used to monitor and control the flow rate of fluid within an industrial process system. Automated industrial systems that process fluid media rely heavily on flow switches to ensure safe and optimal flow rates. Flow switches respond to pre-set flow rate levels and perform two functions when those levels are reached: namely, closing its contacts and turning a specific piece of equipment ON, or opening its contacts and turning a specific piece of equipment OFF.
4. What is the difference between a flow switch and a flow sensor?
Answer: While flow switches and flow sensors both can be used to monitor media flow within a system, the difference between a flow switch and a flow sensor is that a flow sensor can only monitor and display information – flow switches monitor flow and send trip signals and trigger specific actions from machines within the system.
5. What are some of the functions of a flow switch?
Answer: Flow switches perform precise functions based on set requirements. They are capable of stopping a motor when there is no flow as well as triggering the same motor to run once the flow starts. It can sound an alarm when the flow arrests, and it can turn off the alarm when the flow rate reaches an appropriate level.
Since flow switches play such an integral role in many industries, there are a few important considerations.
Measuring flow rate accurately is crucial. This is inferred by calculating the change in dynamic energy or velocity; the velocity, in turn, is dependent upon the pressure differential that forces the liquid through the conduit or pipe. Since the cross-sectional area of a pipe is constant and known, the velocity is a good indication of the flow rate. Calculating the flow rate must be done as it assists in setting flow switches to a pre-determined close function.
In closing, here are some types of flow switches to consider for your specific use.
Vane-Operated Flow Switch
A vane-operated flow switch relies on fluid pushing against an internal paddle. As the flow drops to preset levels, it triggers an internal magnetic mechanical and coupling switch actuation lever which essentially trips the switch.
Variable Area Flow Switch
This device has an internal piston that activates the switch. The flow enters a port and adds pressure to the magnetic poppet; once this pressure hits the preset level, the switch will turn off.
Ultrasonic (Doppler) Flow Switch
Attached to the outside of a pipe, ultrasonic sensors send signals when it detects a change in the flow.
Comments
Post a Comment