Stepper Motor Working Principle advantages, disadvantages and applications
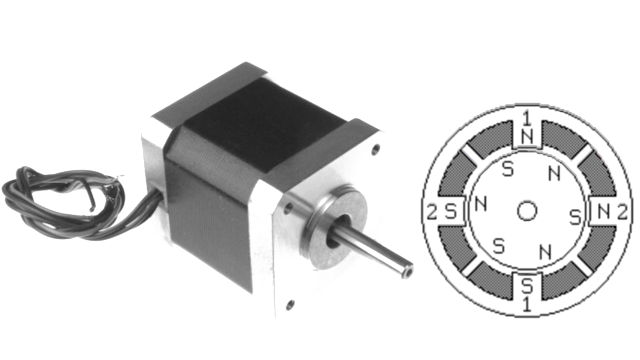
Stepper Motor Introduction The motor which moves in discrete steps is known as the stepper motor. A stepper motor is an electromechanical device it converts electrical power into mechanical power. Also, it is a brushless, synchronous electric motor that can divide a full rotation into an expansive number of steps. Stepper motors operate differently from DC brush motors, which rotate when voltage is applied to their terminals. Stepper motors, on the other hand, effectively have multiple toothed electromagnets arranged around a central gear-shaped piece of iron. The electromagnets are energized by an external control circuit, for example, a microcontroller. The motor’s position can be controlled accurately without any feedback mechanism, as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application. Stepper motors are similar to switched reluctance motors. The stepper motor uses the theory of operation for magnets to make the motor shaft turn a precise distance when a pulse of ...