Different stages involved in the production for sugar industry.
Different stages involved in the production for sugar industry.
Sugar industry is defined as industry which is involved in the production of edible sugar from raw sugar cane and sugar beet.
Different stages in manufacturing process
- Planting and harvesting
- Preparation & Processing
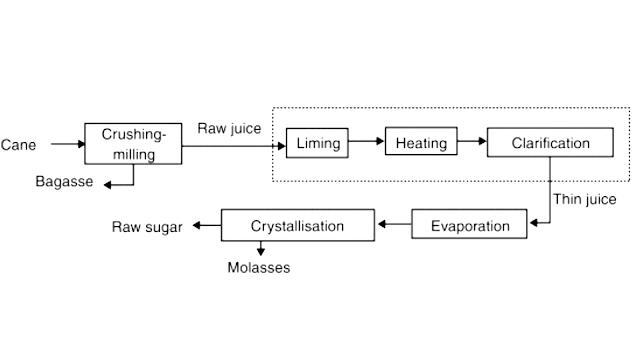
- Juice extraction process
- Purification of juice
- Crystallization
- Centrifuging
- Drying and packing
Planting and harvesting
- Sugar cane requires an average temperature of 24 degrees.
- Black soil is essential.
- The harvested cane stacks are loaded mechanically or physically into trucks or tractors & taken to factory for processing.
Preparation & Processing
- After the sugar cane is arrived at sugar factory,it is unloaded physically or mechanically by using cranes.
- Then it is cleaned or washed.
- Excessive soil are removed and the cane is ready to be milled.
Juice extraction process
- Heavily grooved crusher rollers break the cane & extract a large part of juice.
- Revolving knifes cuts the stalk into chips are supplementary to the crusher.
- The pressing process involves crushing the stalks between the heavy & grooved metal rollers to separate the bagasse.
- As the cane is crushed, hot water (or a combination of hot water and recovered impure juice) is sprayed onto the crushed cane counter currently as it leaves each mill for diluting.
- Extracted juice contains 95% or more of the sucrose present.
Purification of juice
- The clarification process is designed to remove both soluble and insoluble impurities such as sand, soil, and ground rock.
- The process employs lime and heat as the clarifying agents.
- The lime is added to neutralize the organic acids, and the temperature of the juice raised to about 95 degree.
- The mud’s separate from the clear juice through sedimentation.
- The final clarified juice contains about 85 percent water and has the same composition as the raw extracted juice.
- To concentrate the clarified juice, about two-thirds of the water is removed through vacuum evaporation.
- Evaporator stations consist of a series of evaporators, termed multiple-effect evaporators; typically a series of four evaporators.
- Steam from large boilers is used to heat the first evaporator, and the steam from the water evaporated in the first evaporator is used to heat the second Evaporator.
- The evaporator station in cane sugar manufacture typically produces a syrup with about 65 percent solids and 35 percent water.
- Following evaporation, the syrup is clarified by adding lime, phosphoric acid, and filtered in the clarifier.
Crystallization
- Crystallization takes place in a single stage vacuum pan. The syrup is evaporated until saturated with sugar.
- As saturation point has been exceeded, small grains of sugar are added to pan.
- Small grains are called SEED serve as nuclei for the formation of sugar crystal.
- The growth of sugar crystals continues until the pan is full.
- When sucrose concentration reaches the desired level, dense mixture of syrup & sugar crystals are discharged into crystallizers.
- Crystallization continues until syrup & crystals are stirred & cooled.
Centrifuging
- The high speed centrifugal action used to separate the syrup and sugar crystals into raw sugar crystals & molasses done in revolving machine called Centrifuging.
- The machine has cylindrical basket suspended on a spindle, with perforated sides lined with wire cloth inside with metal sheets.
- Basket revolves at 1000 to 1800 RPM.
- The raw sugar is retained in centrifuge basket & molasses passes through the lining.
- Once sugar is centrifuged, it is sent to a granulator for drying & remaining molasses is sent back to next pan.
Drying and packing
- Dump sugar crystals are dried by being tumbled through heated air in a granulator.
Comments
Post a Comment