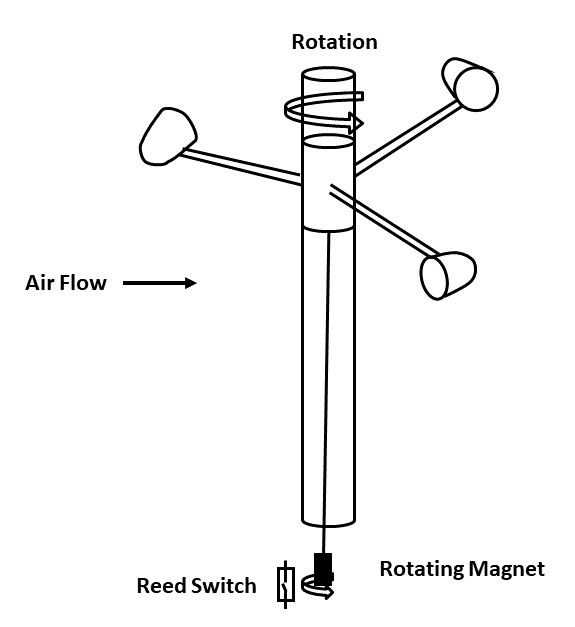
Types of Hygrometer
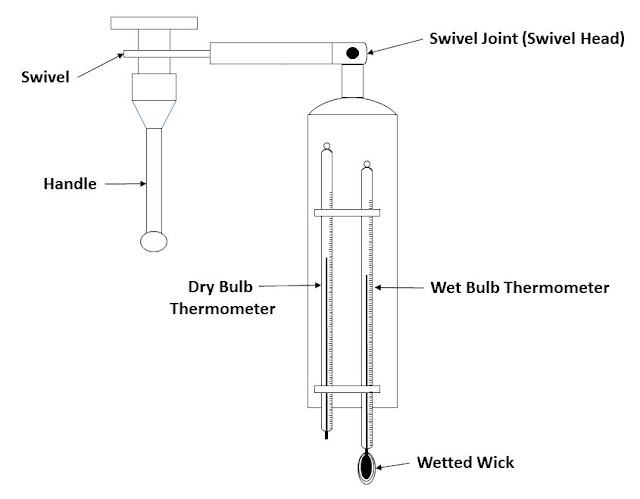
Types of Hygrometer Dry & wet bulb hygrometer. (Psychrometer) Hair hygrometer Sling psychrometer. Chilled mirror dew point hygrometer Dry & wet bulb hygrometer. (Psychrometer) When water or ice covers the bulb of a thermometer (wet-bulb), latent heat is removed from the surface of the bulb as the water evaporates, and the wet-bulb temperature becomes lower than the air (dry-bulb) temperature. At a lower humidity, water evaporates more actively, so that the wet-bulb temperature lowers sharply. The aspirated psychrometer measures humidity by measuring the difference between the dry-bulb temperature and wet-bulb temperature. A psychrometer, or a wet and dry-bulb thermometer, consists of two calibrated thermometers, one that is dry and one that is kept moist with distilled water on a sock or wick. At temperatures above the freezing point of water, evaporation of water from the wick lowers the temperature, such that the wet-bulb thermometer will be at a lower temperature than that