Illustrate the need of following unit operations.1) Pulverization 2) Crystallization 3) Screening 4) Evaporation
Illustrate the need of following unit operations.1) Pulverization 2) Crystallization 3) Screening 4) Evaporation
Pulverization
“Pulverization” (comminution, crushing, grinding) is the process of applying an external force to a (solid) material of a certain size to destroy it and reduce it into pieces that are smaller than the original size. Pulverization has long been done for many materials, including ore, glass, ceramics, grains, paints, and medicines.
Mechanism of pulverization
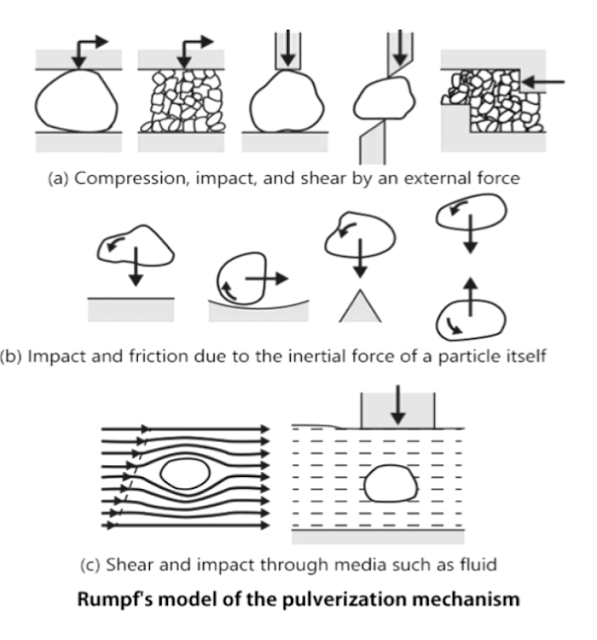
The external force applied to particles can be roughly divided into four types, “compression”, “impact”, “shear”, and “friction”. The actual pulverization mechanism is complicated. Instead of a single type of external force, several types may act on a particle at the same time. In addition, the process is affected in a complicated way by the physical properties of the pulverized material, the pulverization environment, etc. Therefore, it is difficult to clearly explain the pulverization process. Below is a model of force acting on a solid, as proposed by Rumpf.
Screening
Screening is the process by which granulated ore material gets separated into different grades of particle size. In other words, it's a mechanical process that stratifies (divides) particles according to a required size. Mechanical screening, often just called screening, is the practice of taking granulates ore material and separating it into multiple grades by particle size. This practice occurs in a variety of industries such as mining and mineral processing, agriculture, pharmaceutical, food, plastics, and recycling. A method of separating solid particles according to size alone is called screening.
Crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which a solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some of the ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas.
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. The surrounding gas must not be saturated with the evaporating substance. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide with each other.
Comments
Post a Comment