Humidity, Soil Moisture & Rain Sensor
Humidity, Soil Moisture & Rain Sensor
Humidity Sensor
A humidity sensor is an electronic device that measures the humidity in its environment and converts its findings into a corresponding electrical signal.Relative humidity is calculated by comparing the live humidity reading at a given temperature to the maximum amount of humidity for air at the same temperature.
Introduction
Humidity Sensors are the low cost-sensitive electronic devices used to measure the humidity of the air. These are also known as Hygrometers. Humidity can be measured as Relative humidity, Absolute humidity, and Specific humidity. Based on the type of humidity measured by sensor, these are classified as Relative Humidity sensor and Absolute Humidity sensor.
Based on the parameters used to measure humidity, these sensors are also classified as Capacitive Humidity Sensor, Resistive Humidity Sensor, and Thermal Conductivity Humidity Sensor.
Some of the parameters to consider while choosing these sensors are the Accuracy, Linearity, Reliability, Repeatability and Response time.
What is a Humidity Sensor?
A humidity sensor is an electronic device that measures the humidity in its environment and converts its findings into a corresponding electrical signal. Humidity sensors vary widely in size and functionality; some humidity sensors can be found in handheld devices (such as smartphones), while others are integrated into larger embedded systems (such as air quality monitoring systems). Humidity sensors are commonly used in the meteorology, medical, automobile, HVAC and manufacturing industries.
Humidity sensors can be divided into two groups, as each category uses a different method to calculate humidity: relative humidity (RH) sensors and absolute humidity (AH) sensors. Relative humidity is calculated by comparing the live humidity reading at a given temperature to the maximum amount of humidity for air at the same temperature. RH sensors must therefore measure temperature in order to determine relative humidity. In contrast, absolute humidity is measured without reference to temperature.
The two most common RH sensors are the capacitive and resistive humidity sensors. Capacitive sensors use two electrodes to monitor the capacitance (i.e. the ability to store an electric charge) of a thin metal strip placed between them. The metal’s capacitance increases or decreases at a rate that is directly proportional to the change of humidity in the sensor’s environment. The difference in charge (voltage) generated by an increase in humidity is then amplified and sent to the embedded computer for processing. Resistive humidity sensors operate on a different principle. These sensors utilize a small polymer comb that increases and decreases in size as the humidity changes, which directly affects the system’s ability to store charge.
Thermal humidity sensors are used to measure absolute humidity. Unlike RH sensors, thermal humidity sensors utilize two probes, one to measure dry nitrogen and one to measure the air of its surrounding environment. When humidity is collected on the exposed probe, the difference in thermal conductivity is perceived by the sensor, and AH is calculated.
Types of humidity sensors
- Capacitive
- Resistive
- Thermal
Capacitive
A capacitive humidity sensor measures relative humidity by placing a thin strip of metal oxide between two electrodes. The metal oxide’s electrical capacity changes with the atmosphere’s relative humidity. Weather, commercial and industries are the major application areas.
The capacitive type sensors are linear and can measure relative humidity from 0% to 100%. The catch here is a complex circuit and regular calibration. However, for designers this a lesser hassle over precise measurement and hence these dominate atmospheric and process measurements. These are the only types of full-range relative humidity measuring devices down to 0% relative humidity. This low-temperature effect often leads to them being used over wide temperature ranges without active temperature compensation.
Resistive
Resistive humidity sensors utilize ions in salts to measure the electrical impedance of atoms. As humidity changes, so do the resistance of the electrodes on either side of the salt medium.
Thermal
Two thermal sensors conduct electricity based upon the humidity of the surrounding air. One sensor is encased in dry nitrogen while the other measures ambient air. The difference between the two measures the humidity.
Working Principle of Humidity Sensor
Relative humidity sensors usually contain a humidity sensing element along with a thermistor to measure temperature. For a capacitive sensor, the sensing element is a capacitor. Here the change in electrical permittivity of the dielectric material is measured to calculate the relative humidity values.
Low resistivity materials are used for the construction of a Resistive sensor. This resistive material is placed on top of two electrodes. Change in the resistivity value of this material is used to measure the change in humidity.
Salt, solid electrolytes and conductive polymers are the examples of resistive material used in Resistive sensor. Thermal conductive sensors measure Absolute humidity values.
Applications
- Industrial process control systems. Storage and warehouses
- Climate control for green houses
- Meteorological applications
- Office automation, room comfort control
- Automotive cabin air control
- Home appliances, Air conditioners
- Food processing
- Medical applications
- Chicken Coops, Pig Barns
Soil Moisture Sensor
What is a Soil Moisture Sensor?
The soil moisture sensor is one kind of sensor used to gauge the volumetric content of water within the soil. As the straight gravimetric dimension of soil moisture needs eliminating, drying, as well as sample weighting. These sensors measure the volumetric water content not directly with the help of some other rules of soil like dielectric constant, electrical resistance, otherwise interaction with neutrons, and replacement of the moisture content.
The relation among the calculated property as well as moisture of soil should be adjusted & may change based on ecological factors like temperature, type of soil, otherwise electric conductivity. The microwave emission which is reflected can be influenced by the moisture of soil as well as mainly used in agriculture and remote sensing within hydrology.
These sensors normally used to check volumetric water content, and another group of sensors calculates a new property of moisture within soils named water potential. Generally, these sensors are named as soil water potential sensors which include gypsum blocks and tensiometer.
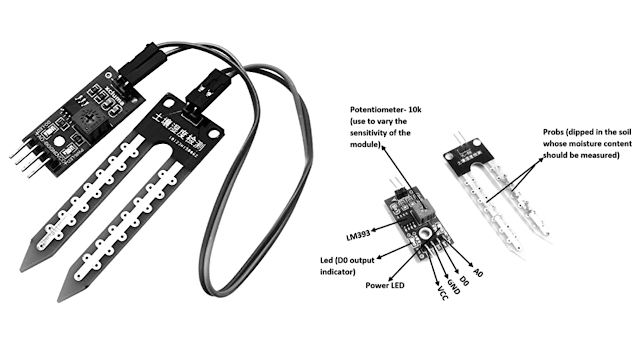
Soil Moisture Sensor Pin Configuration
The FC-28 soil moisture sensor includes 4-pins
- VCC pin is used for power
- A0 pin is an analog output
- D0 pin is a digital output
- GND pin is a Ground
This module also includes a potentiometer that will fix the threshold value, & the value can be evaluated by the comparator-LM393. The LED will turn on/off based on the threshold value.
How the Sensor Works
The Soil Moisture Sensor uses capacitance to measure dielectric permittivity of the surrounding medium. In soil, dielectric permittivity is a function of the water content. The sensor creates a voltage proportional to the dielectric permittivity, and therefore the water content of the soil.
The sensor averages the water content over the entire length of the sensor. There is a 2 cm zone of influence with respect to the flat surface of the sensor, but it has little or no sensitivity at the extreme edges. The figure above shows the electromagnetic field lines along a cross-section of the sensor, illustrating the 2 cm zone of influence.
Working Principle
This sensor mainly utilizes capacitance to gauge the water content of the soil (dielectric permittivity). The working of this sensor can be done by inserting this sensor into the earth and the status of the water content in the soil can be reported in the form of a percent.
This sensor makes it perfect to execute experiments within science courses like environmental science, agricultural science, biology, soil science, botany, and horticulture.
Specifications
- The required voltage for working is 5V
- The required current for working is <20mA
- Type of interface is analog
- The required working temperature of this sensor is 10°C~30°C
Soil Moisture Sensor Applications
- Agriculture
- Landscape irrigation
- Research
- Simple sensors for gardeners
Rain Sensor
What is a Rain Sensor?
A rain sensor is one kind of switching device which is used to detect the rainfall. It works like a switch and the working principle of this sensor is, whenever there is rain, the switch will be normally closed.
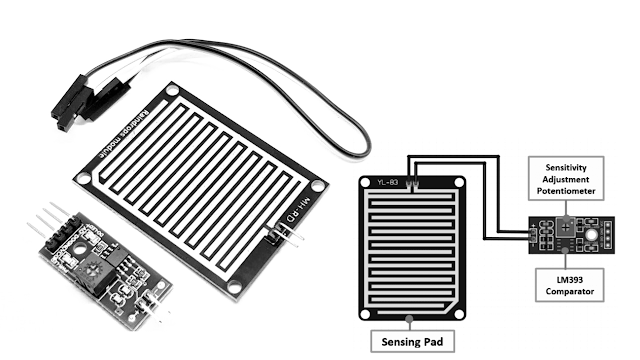
Rain Sensor Module
The rain sensor module/board is shown below. Basically, this board includes nickel coated lines and it works on the resistance principle. This sensor module permits to gauge moisture through analog output pins & it gives a digital output while moisture threshold surpasses.
This module is similar to the LM393 IC because it includes the electronic module as well as a PCB. Here PCB is used to collect the raindrops. When the rain falls on the board, then it creates a parallel resistance path to calculate through the operational amplifier.
This sensor is a resistive dipole, and based on the moisture only it shows the resistance. For example, it shows more resistance when it is dry and shows less resistance when it is wet.
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of this sensor is shown below. This sensor includes four pins which include the following.
- Pin1 (VCC): It is a 5V DC pin
- Pin2 (GND): it is a GND (ground) pin
- Pin3 (DO): It is a low/ high output pin
- Pin4 (AO): It is an analog output pin
How Rain Sensor works?
The working of the rain sensor is pretty straightforward.The sensing pad with series of exposed copper traces, together acts as a variable resistor (just like a potentiometer) whose resistance varies according to the amount of water on its surface.
This resistance is inversely proportional to the amount of water:
- The more water on the surface means better conductivity and will result in a lower resistance.
- The less water on the surface means poor conductivity and will result in a higher resistance.
The sensor produces an output voltage according to the resistance, which by measuring we can determine whether it’s raining or not.
Specifications
- This sensor module uses good quality of double-sided material.
- Anti-conductivity & oxidation with long time use
- The area of this sensor includes 5cm x 4cm and can be built with a nickel plate on the side
- The sensitivity can be adjusted by a potentiometer
- The required voltage is 5V
- The size of the small PCB is 3.2cm x 1.4cm
- For easy installation, it uses bolt holes
- It uses an LM393 comparator with wide voltage
- The output of the comparator is a clean waveform and driving capacity is above 15mA
Applications
- This sensor is used as a water preservation device and this is connected to the irrigation system to shut down the system in the event of rainfall.
- This sensor is used to guard the internal parts of an automobile against the rainfall as well as to support the regular windscreen wiper’s mode.
- This sensor is used in specialized satellite communications aerials for activating a rain blower over the opening of the aerial feed, to get rid of water droplets from the mylar wrap to keep pressurized as well as dry air within the waveguides.
Example
Automatic Rain Sensing Windshield Wiper
Introduction
- The RainTracker automotive rain sensor, senses rain or snow hitting the windshield, and automatically runs the wipers at the right speed.
- we don't have to take our hands off the wheel, or constantly adjust the speed of the wipers as road conditions change.
- A rain sensor or rain switch is a switching device activated by rainfall
- In this the sensor projects infrared light into the windshield at a 45-degree angle
- If the glass is dry, than most of this light is reflected back into the sensor by the front of the windshield.
- If water droplets are on the glass, than it reflect the light in different direction the wetter the glass, the less light makes it back into the sensor.
- The electronics and software in the sensor turn on the wipers when the amount of light reflected onto the sensor.
- Software sets the speed of the wipers based on how fast the moisture builds up between wipes. It can operate the wipers at any speed.
High Level System Diagram
- In this battery supplies the power to the sensor
- Then the wiper motor is automatically on during the time of rainfall
- This sensor is fixed in the vehicle glass
- It senses the rainfall and giving control signal to the control unit
- The control unit activate the wiper automatically
- The rain sensor works on the principle of using water for completing its circuit
- So when rain falls on it it’s circuit gets completed.
NE555 IC
Circuit diagram
Working
The circuit presented here is not using the optical technology It is built around the famous NE555 timer IC that is working as a monostable multivibrator here. The circuit is using a handmade sensor to detect raindrops. The sensor can be made by attaching 2 wires of 0.5 inch. When two wire in the hand made sensor will detect raindrops then the output of the NE555 IC at the output pin 3 will goes high Activates the relay for a set time period and after that time period is over the relay will switch off again. The activation time period of the relay is few seconds but it can be increased by increasing the value of the capacitor.
- Detect intensity of rainfall
- Detect rainfall on windshield
- Improve safety by decreasing driver distraction
- Automatically activate windshield wipers once rainfall is detected
Advantage
- Sensor cost is low
- High accuracy
- Automatic Windshield Wipers
- Automatic Braking
- Hands-Free Calling
- Less power consumption
- Automotive Safety and Convenience
Disadvantage
- Additional cost is required in case optical sensor is used
- This system is applied in the case of water falling on the glass only
Applications
- Rain sensing wipers are great convenience feature in a luxury car
- More useful in marine applicati ons.
- It is use in aircraft
- Fit in existing housing area









Comments
Post a Comment