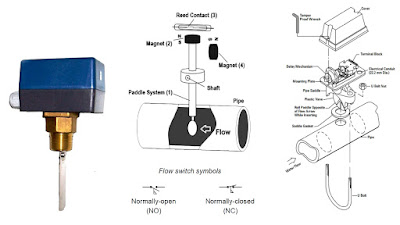
Feedback-feed-forward control scheme used in heat exchanger for temperature control

Feedback-feed-forward control scheme used in heat exchanger for temperature control Feedback control Feedback control is a control action of altering the manipulated variable in response to the deviation between the controlled variable and its set point in such a way to eliminate the deviation. Temperature Control Using Feedback Control Consider a process outlet temperature control problem in a furnace. The furnace is used to heat the process fluid stream and its outlet temperature is to be controlled. In feedback control, the outlet temperature is measured and it is compared against the reference set point. The deviation between the desired and measured temperatures is found. The flow rate of the fuel gas is adjusted in accordance with the magnitude of deviation by the controller through the control valve. The outlet stream temperature is kept at the desired value by controlling fuel gas flow rate Limitations of feedback control Feedback control takes corrective action only after the