Infrared Sensor
Infrared Sensor(IR Sensor)
An infrared sensor is an electronic device, that emits in order to sense some aspects of the surroundings. An IR sensor can measure the heat of an object as well as detects the motion. These types of sensors measure only infrared radiation, rather than emitting it that is called a passive IR sensor.
Introduction
IR technology is used in daily life and also in industries for different purposes. For example, TVs use an IR sensor to understand the signals which are transmitted from a remote control. The main benefits of IR sensors are low power usage, their simple design & their convenient features. IR signals are not noticeable by the human eye. The IR radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum can be found in the regions of the visible & microwave. Usually, the wavelengths of these waves range from 0.7 µm 5 to 1000µm. The IR spectrum can be divided into three regions like near-infrared, mid, and far-infrared. The near IR region’s wavelength ranges from 0.75 – 3µm, the mid-infrared region’s wavelength ranges from 3 to 6µm & the far IR region’s infrared radiation’s wavelength is higher than 6µm.
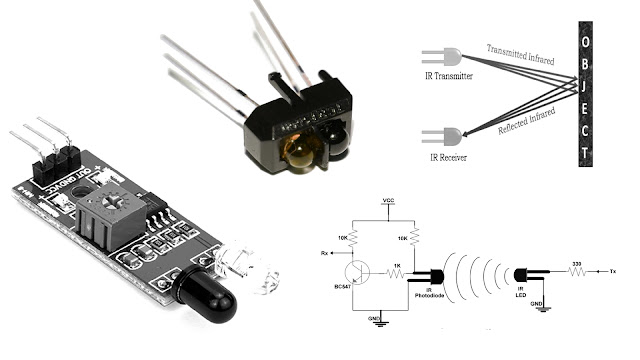
An infrared sensor is an electronic device, that emits in order to sense some aspects of the surroundings. An IR sensor can measure the heat of an object as well as detects the motion. These types of sensors measure only infrared radiation, rather than emitting it that is called a passive IR sensor. Usually, in the infrared spectrum, all the objects radiate some form of thermal radiation.These types of radiations are invisible to our eyes, which can be detected by an infrared sensor. The emitter is simply an IR LED (Light Emitting Diode) and the detector is simply an IR photodiode that is sensitive to IR light of the same wavelength as that emitted by the IR LED. When IR light falls on the photodiode, the resistances and the output voltages will change in proportion to the magnitude of the IR light received.
Types of Infrared Sensor
Infrared sensors are classified into two types like
Active IR sensor and
Passive IR sensor.
Active IR Sensor
This active infrared sensor includes both the transmitter as well as the receiver. In most of the applications, the light-emitting diode is used as a source. LED is used as a non-imaging infrared sensor whereas the laser diode is used as an imaging infrared sensor.These sensors work through energy radiation, received & detected through radiation. Further, it can be processed by using the signal processor to fetch the necessary information. The best examples of this active infrared sensor are reflectance and break beam sensor.
Passive IR Sensor
The passive infrared sensor includes detectors only but they don’t include a transmitter. These sensors use an object like a transmitter or IR source. This object emits energy and detects through infrared receivers. After that, a signal processor is used to understand the signal to obtain the required information.
The best examples of this sensor are pyroelectric detector, bolometer, thermocouple-thermopile, etc.
These sensors are classified into two types like
Thermal IR sensor and
Quantum IR sensor.
Thermal IR sensor
The thermal IR sensor doesn’t depend on wavelength. The energy source used by these sensors is heated. Thermal detectors are slow with their response and detection time.
Quantum IR sensor
The quantum IR sensor depends on the wavelength and these sensors include high response and detection time. These sensors need regular cooling for specific measurements.
Advantages
- It uses less power
- The detection of motion is possible in the presence or absence of light approximately with equal reliability.
- They do not need contact with the object for detection
- There is no data leakage because of the ray direction
- These sensors are not affected by oxidation & corrosion
- Noise immunity is very strong
Disadvantages
- Line of sight is required
- Range is limited
- These can be affected by fog, rain, dust, etc
- Less data transmission rate
Application
- OBSTACLE DETECTOR
- IN ROBOTICS
- BRIGHTNESS COMPARISON
- DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
Comments
Post a Comment