Level sensor working principle and applications
Level Sensors
A level sensor is a device that is designed to monitor, maintain, and measure liquid (and sometimes solid) levels. Once the liquid level is detected, the sensor converts the perceived data into an electric signal. Level sensors are used primarily in the manufacturing and automotive industries, but they can be found in many household appliances as well, such as ice makers in refrigerators.
What is a Liquid Level Sensor?
Liquid level sensors, also called liquid level switches, are designed to change state when immersed in a liquid. They are used to determine if a liquid or oil exists at a particular level in a container.
Introduction
Level sensors are useful devices that are used to detect the level of substances such as liquids, powders and granular materials. There is a wide range of level sensors and they are all used in different industries. Some level sensors can be used for any fluid and others can only be used for certain substances.
Level sensors are used to measure substances that are inside a container or in their natural state, e.g. rivers.
Level sensors are used in the following industries:
- Oil Manufacturing Plants
- Water Treatment
- Paper and Pulp Production Divisions
- Petrochemical and Chemical Making & Refinery Units
- Waste Material Handling Industry
- Beverage and Food Manufacturing Factories
- Pharmaceutical Processes
- Power Generating Plants
Below is a list of the most common level sensors:
- Reflex level sensor
- Tank level sensor
- Bi-colour level sensor
- Transparent level sensor
There are various technologies that are used in the level sensor market. Ultrasonic is the most popular technology; this is due to that fact that ultrasonic sensors are small, mobile and they have no moving parts; they are easy to use, affordable and they do not require much maintenance. Ultrasonic sensors are used to measure thick substances and they can be used in extreme conditions.
Level Sensor Classification
Level Sensors can be broken into two classifications;
- Point level measurement
- Continuous level measurement
Point level measurement indicates when a product is present at a certain point and continuous level measuring indicates the continuous level of a product as it rises and falls.
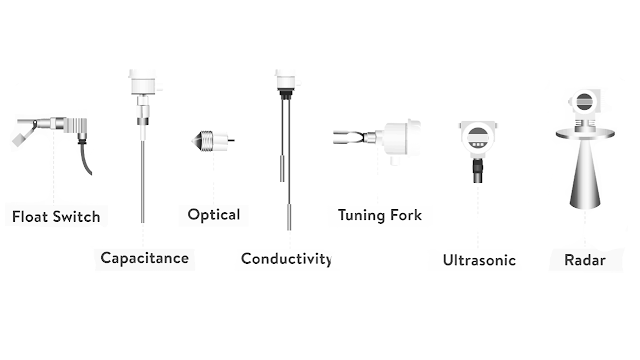
The sensors for point level indication are:
- Capacitance
- Optical
- Conductivity
- Vibrating (Tuning fork)
- Float Switch
The sensors for continuous level measuring are:
- Ultrasonic
- Radar (Microwave)
Point Level Measurement Sensors
1. Capacitance Level Sensors
These sensors are used to detect the liquid levels like slurries and aqueous liquids. They are operated by using a probe for checking level changes. These level changes are transformed into analog signals. The probes are generally made of conducting wire by PTFE insulation. But, stainless steel probes are extremely responsive and hence they are appropriate for measuring non-conductive substance granular or materials with low dielectric constant. These types of sensors are very simple to use and clean as they do not have any moving components.
Pros and Cons
- Solid-state, compact, can be non-invasive, accurate
- Can only be used in certain liquids, May require calibration
Applications
They are commonly used in applications like Tank level monitoring in chemical, water treatment, food, battery industries and involving high pressure and temperature.
2. Optical Level Sensors
Optical level sensors are used to detect liquids including poised materials, interface between two immiscible liquids and the occurrence of sediments. They are worked based on the changes of transmission in infrared light emitted from an IR LED. The interference from the produced light can be reduced by using a high energy IR diode and pulse modulation methods.
Continuous optical level sensors, on the other hand, use the highly intense laser light that can infuse dusty environments and notice liquid substances.
Pros and Cons
- Compact, high pressure, no moving parts, and capability of temperature, can notice tiny amounts of liquids.
- Invasive as the sensor needs get in touch with the liquid needs power, certain wide substances can reason coating on the Prism.
Applications
They are commonly used in applications like leak detection and tank level measurement
3. Conductivity (Resistance) Level Sensor
Another style of point level sensor is conductivity or resistance.
A conductivity or resistance sensor uses a probe to read conductivity. The probe has a pair of electrodes and applies alternating current to them.
When a liquid covers the probe its electrodes form a part on an electric circuit, causing current to flow which signals a high or low level.
The advantages of using a conductivity level sensor are:
- There are no moving parts
- They are low cost
- Fairly easy to use
The disadvantages are:
- They are invasive (meaning they must touch the product being sensed)
- They only sense conductive liquids
- The probe will erode over time
Appropriate use for these sensors would be for signaling high or low levels.
4. Vibrating (Tuning Fork) Level Sensor
Vibrating or tuning forks is another type of point level sensor.
They use a fork-shaped sensing element with two tines. The fork vibrates at its natural resonant frequency. As the level changes, the frequency of the fork will change detecting the level.
These sensors are:
- Cost effective and compact
- Invasive to the product, meaning they have to touch the material to sense the level
- Easy to install
- Essentially maintenance-free
They have unlimited uses based on the material that they can sense. Mining, food and beverage, and chemical processing industries use these sensors for their applications.
5. Float Switch
The last point level sensor that we will talk about is a float switch.
Float switches use a float, a device that will raise or lower when a product is applied or removed, which will open or close a circuit as the level raises or lowers moving the float.
Advantages of a float switch are:
- They are non powered device
- They provide a direct indication
- They are inexpensive
Disadvantages are:
- They are invasive to the product
- They have moving parts
- They can be large in size
Float switches will only give an indication for a high or low level, they cannot measure a variable level. A great use for float switches is in liquid storage tanks for high or low-level indication.
Continuous Level Measurement Sensors
1. Ultrasonic Level Sensors
Ultrasonic level sensors are used to detect the levels of sticky liquid substances and bulkiness materials as well. They are worked by producing audio waves at the range of frequency from 20 to 200 kHz. These waves are then replicated back to a transducer. The ultrasonic sensor’s response is influenced by turbulence, pressure, moisture, and temperature. In addition, the transducer is necessary to be increased appropriately to obtain a better response.
Pros and Cons
- Compact, cost-effective
- Invasive, numbers of users are limited
The advantage of using this type of sensor is that:
- These sensors have no moving parts
- They are compact
- They are reliable
- Non-invasive (Non-contact)
- Unaffected by the properties of the material they are sensing
- Self-cleaning because of the vibrations they give off
The disadvantage of using this type of sensor is that:
- They can be expensive
- In some situations, the environment can have a negative effect on them
Applications
The ultrasonic level sensors are used to control the liquid level, fine-grained solids within mining and powders, food and beverage industries and chemical processing.
2. Microwave Optical Sensors
These types of sensors are used for applications like varying temperature, pressure, dirty and moist environments, as microwaves can easily go through under these situations without involving air molecules for energy transmission. Microwave Optical sensors can notice conductive water & metallic substances. The measurements are accepted using time domain or pulse reflectometry.
Pros and Cons
- No calibration required, very accurate, multiple output options
- Costly, limited detection range, and can be affected by the environment.
The advantages of radar sensors are that:
- They are not affected by temperature, pressure or dust
- They can also measure liquids, pastes, powders, and solids
- They are very accurate and require no calibration
- They are non-invasive because they do not have to touch the product that it is sensing
The disadvantages of radar sensors are that:
- They are expensive
- They have a limited detection range
Applications
- They are commonly used in applications like vaporous, Moist, and dusty environments.
- They are also used in systems in which temperatures differ.







Comments
Post a Comment