Elaborate Working of Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger?
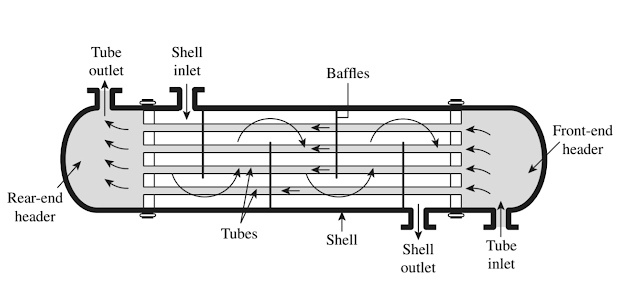
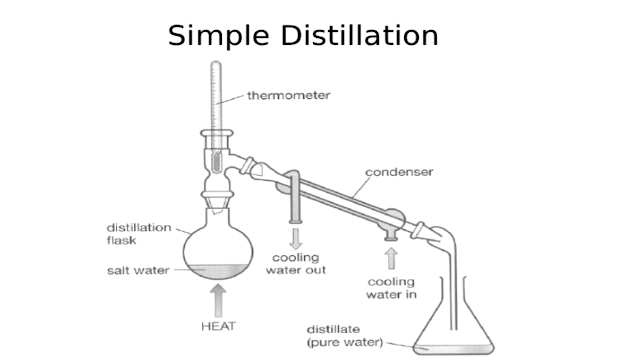
Elaborate Working of Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger. Working of Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger Above figure shows the typical configuration of shell and tube heat exchangers, with labels for easy reading. As previously explained, the fundamental point of shell and tube heat exchangers is to pass a hot fluid through a cold fluid without mixing them, so that only their heat is transferred. The above diagram shows two inlets and two outlets, where each fluid starts at their respective inlet and exits the device at their outlets. The tube-side flow passes through the tube bundle (secured by metal plates known as tubesheets or tubeplates) and exits the tube outlet. Similarly, the shell-side flow starts at the shell inlet, passes over theses tubes, and exits at the shell outlet. The headers on either side of the tube bundle create reservoirs for the tube-side flow and can be split into sections according to specific heat exchanger types. Each tube contains an insert known as a turbulator